Flutter
Introduction
Why Flutter created in 2017
- Compiles to native, JIT and Ahead of Time
- Fast Development
- Single Code Base
- Uses Dart
Resources is https://github.com/simoales/flutter
Installation
Flutter
You can switch versions of flutter using the channel option where there are options of master, dev, beta etc. See https://github.com/flutter/flutter/wiki/Flutter-build-release-channels
sudo snap install flutter --classic
sudo snap install flutter-gallery
flutter channel dev
flutter upgrade
flutter config --enable-linux-desktop
You will need to specify the path to android studio
flutter config --android-studio-dir="/opt/android-studio-4.1/android-studio"
Android Studio
For Android Studio the flutter SDK will be in /home/(username)/snap/flutter/common/flutter
Flutter doctor
You can run flutter doctor to see if all went well. This is what I got
flutter doctor
[✓] Flutter (Channel dev, 1.25.0-8.0.pre, on Linux, locale en_NZ.UTF-8)
[✓] Android toolchain - develop for Android devices (Android SDK version 30.0.3)
[✓] Linux toolchain - develop for Linux desktop
[!] Android Studio (not installed)
[✓] VS Code (version 1.52.0)
[✓] Connected device (1 available)
Creating a Project
In VS Code run flutter doctor and then flutter new project. Project names must be in lower case. e.g. hello_flutter. This opens a new VS Code with the project. The import contains the widgets to use and the rest just configures the widgets on the screen. I.E. Text is like a <Text /> tag in react or angular.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(Center(
child: Text("Fred Was Ere",
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
style: TextStyle(backgroundColor: Colors.blue)),
));
}
When familar we can create a project with the flutter cli
flutter create app_widgets
A Bigger Example
So a bigger example might be
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MaterialApp(
title: "My lovely App",
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("App Bar Title"),
),
body: Material(
color: Colors.deepPurple,
child: Center(
child: Text(
"Fred Was Ere",
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontSize: 36.0),
),
),
),
),
));
}
Classes
Things are getting a big large so we need to break the code down. We do this by writing our own classes. We can derive a class from StatelessWidget to do this.
class MyWidget extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: "My lovely App",
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("App Bar Title"),
),
body: Material(
color: Colors.deepPurple,
child: Center(
child: Text(
"Fred Was Ere",
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontSize: 36.0),
),
),
),
),
);
}
}
Fat Arrow
Dart supports the fat arrow approach so we can so
import './screens/home.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyWidget());
}
Can become
import './screens/home.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyWidget());
Adding Logic
No surprises here. We can add functions within the class declaration.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class Home extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Material(
color: Colors.deepPurple,
child: Center(
child: Text(
sayHello(),
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontSize: 36.0),
),
),
);
}
String sayHello() {
var hello;
DateTime now = DateTime.now();
if (now.hour < 12) {
hello = "Good Morning";
} else if (now.hour < 18) {
hello = "Good Afternoon";
} else {
hello = "Good Evening";
}
return hello;
}
}
Basic Widgets and Concepts
The basic widgets and Concepts are
- Container
- Text
- Row & Column
- Image
- RaisedButton
- AlertDialog
- Box Constraints
- Size, Margin and Padding
Containers
They are as they sound. It is worth noting the width and height are controlled by the parent. Look at https://flutter.io/layout. To bypass the constraint of the parent you need to wrap your widget in a widget which supports this. E.g. Center widget.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class Home extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Center(
child: Container(
width: 192.0,
height: 96.0,
alignment: Alignment.center,
color: Colors.deepOrangeAccent,
child: Text(
"Pizza",
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
),
));
}
}
Margins And Padding
Margins and Paddings use the EdgeInsets.All and EdgeInsets.Only constructor. So to set a margin we can do.
...
child: Container(
width: 192.0,
height: 96.0,
margin: EdgeInsets.only(left:50.0),
padding: EdgeInsets.All(10.0),
...
Fonts
Copy the fonts to a directory. The file pubspec.yaml contains the configurations.
fonts:
- family: Oxygen
fonts:
- asset: fonts/Oxygen-Regular.ttf
- asset: fonts/Oxygen-Bold.ttf
weight: 700
- asset: fonts/Oxygen-Light.ttf
weight: 300
Now we can use the font with the Text Widget
...
child: Text(
"Pizza",
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
style: TextStyle(
fontFamily: 'Oxygen',
fontWeight: FontWeight.w300,
),
...
Rows and Columns
These seem to work the same as flex box.
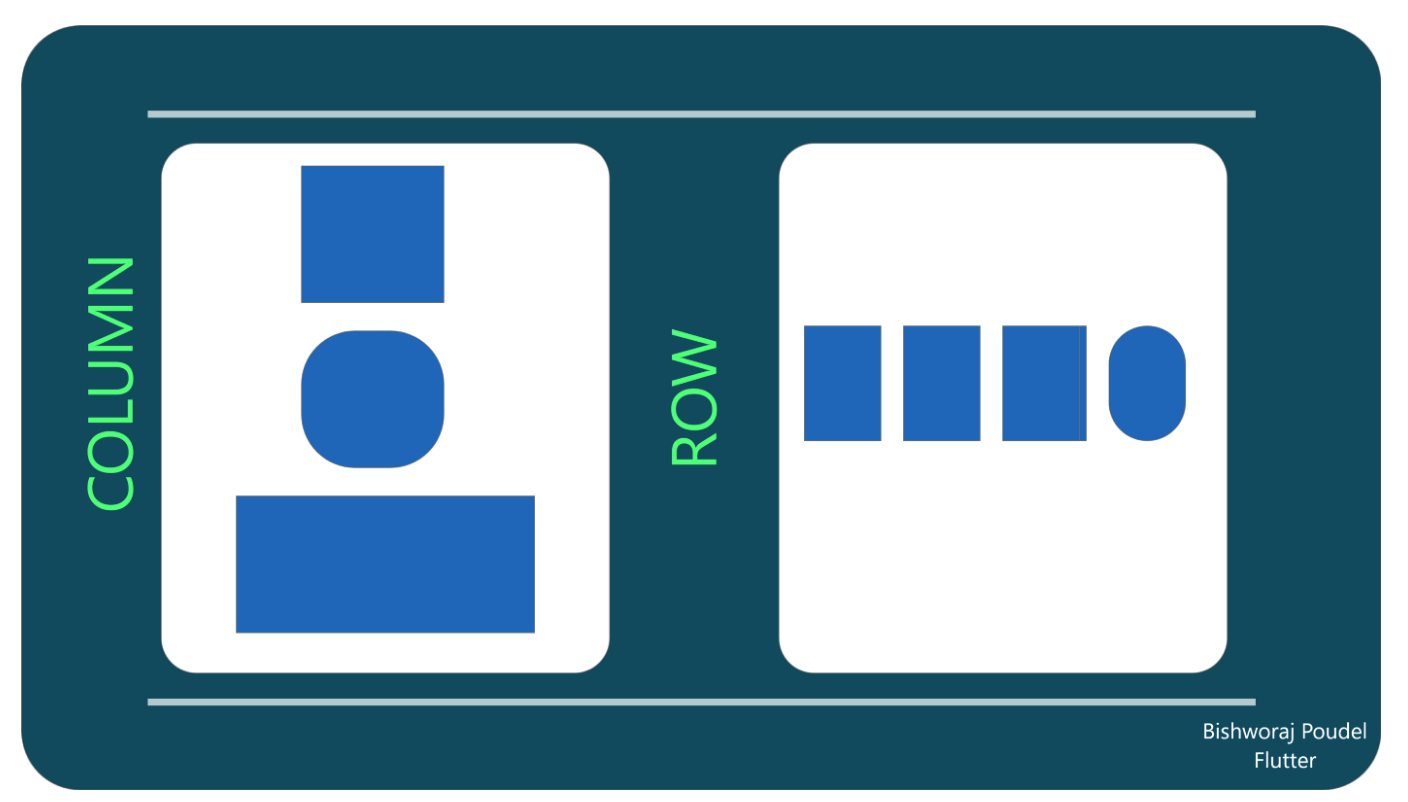
...
child: Row(
children: <Widget>[
Text(
"Margherita",
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
style: TextStyle(
fontFamily: 'Oxygen',
fontWeight: FontWeight.w300,
),
),
Text(
"Tomato, Mozzarella, Basil",
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
style: TextStyle(
fontFamily: 'Oxygen',
fontWeight: FontWeight.w300,
),
),
],
),
...
The result is items which overflow the row because the text exceeds the width of the phone.

Expanded
Adding the expanded keyword makes the text content wrap.
