Test Driven Development
Introduction
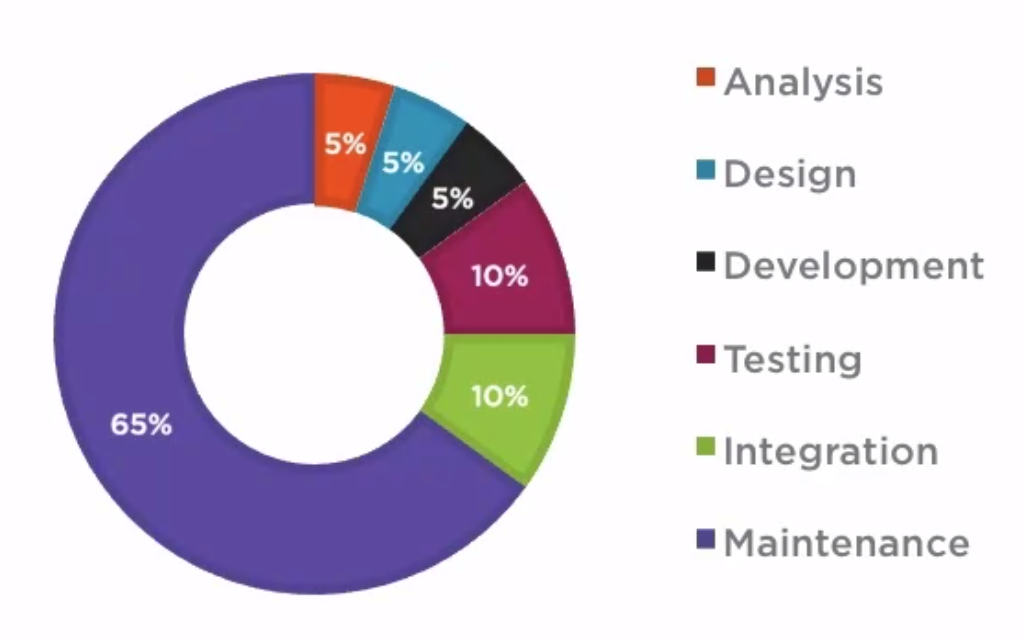
Costs
The cost of software according to this course was
 Tests are split into three categories
Tests are split into three categories
- Does what was asked for
- Responds appropriately to bad input
- Acceptable Performance
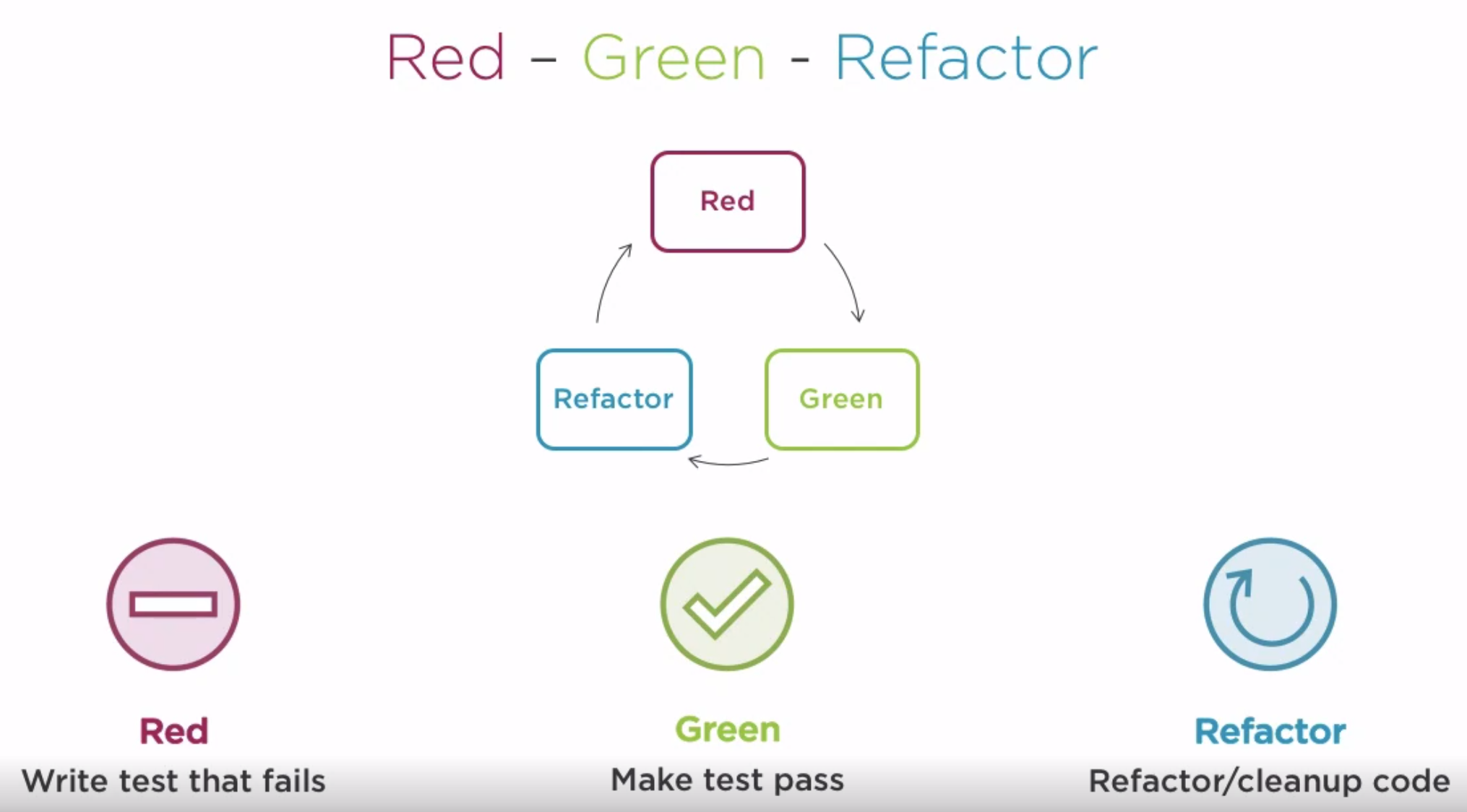
Red Green Refactor
Start by writing tests with no code, write until test pass, refactor code. This is an iterative approach.
Benefits
- Requirements are verified by the tests
- Regression issues raised early
- Costs of maintenance is lowered
- Design first, when writing the tests first we are designing what they want
- Reduces over engineering
- Easy to know where you are in the project
Different Types of Testing
Types of Testing
- Unit Testing
- Functional Testing (UI/End-to-End)
- Integrating Testing
- User Acceptance Testing
Testing Approaches
- Black Box testing (testing the interface)
- White Box testing (testing internal aspects)
Tools
Some well known tools are
- Selenium
- Watir
- VS Coded UI
- Test Studio (Telerik)
- Silk Test (Micro Focus)
Terminology
- Test
- Test Suite (Group of tests)
- Before/After hooks to set up and tear down
- Assert, eg. isTrue, isNull, areEqual
- Test Execution
- Test Runner (async/sync)
Example Fizz Buzz
Requirements
This has the following requirements Given a positive number Divisible by 3 => "Fizz" Divisible by 5 => "Buzz" Divisible by 3 & 5 => "Fizz Buzz" Otherwise => Number
Step 1
Create initial test
public FizzBuzzTests() {
_fizzBuzzService = new FizzBuzzService();
}