Verilog Language: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
=2 to 1 Multiplexer= | =2 to 1 Multiplexer= | ||
This example shows the 3 approaches we can use to describe the hardware | This example shows the 3 approaches we can use to describe the hardware | ||
==Gate Level== | ==Gate Level== | ||
This was quite useful as I have some knowledge of gates and boolean logic so it starts to make a bit of sense in verilog. Here is the truth table for the 2 to 1 multiplexer<br> | This was quite useful as I have some knowledge of gates and boolean logic so it starts to make a bit of sense in verilog. Here is the truth table for the 2 to 1 multiplexer<br> | ||
| Line 18: | Line 17: | ||
To model this at the gate level we could do this<br> | To model this at the gate level we could do this<br> | ||
[[File:Verilog example1b.png| 400px]]<br> | [[File:Verilog example1b.png| 400px]]<br> | ||
=Dataflow Level= | |||
And now the Dataflow level. This does look a lot like boolen logic and is very unreadable.<br> | |||
[[File:Verilog example1c.png| 400px]] | |||
=Dataflow Level= | |||
=Sequential Logic= | =Sequential Logic= | ||
Sequential logic uses memory and state | Sequential logic uses memory and state | ||
Revision as of 06:27, 17 December 2024
Introduction
This page is meant to help understand how to approach the language. There are three levels of abstraction.
Way to describe Hardware
- Gate Level
- Dataflow Level
- Behavioral Level
Types of Logic
- Combinational Logic
- Sequential Logic
Combinational Logic
This is where the outputs are a simple function of the inputs. (Sounds like pure functions
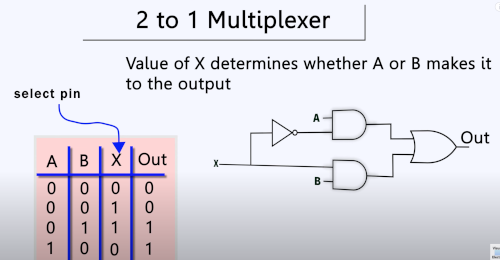
2 to 1 Multiplexer
This example shows the 3 approaches we can use to describe the hardware
Gate Level
This was quite useful as I have some knowledge of gates and boolean logic so it starts to make a bit of sense in verilog. Here is the truth table for the 2 to 1 multiplexer
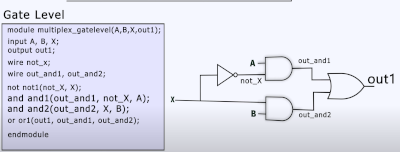
To model this at the gate level we could do this
Dataflow Level
And now the Dataflow level. This does look a lot like boolen logic and is very unreadable.
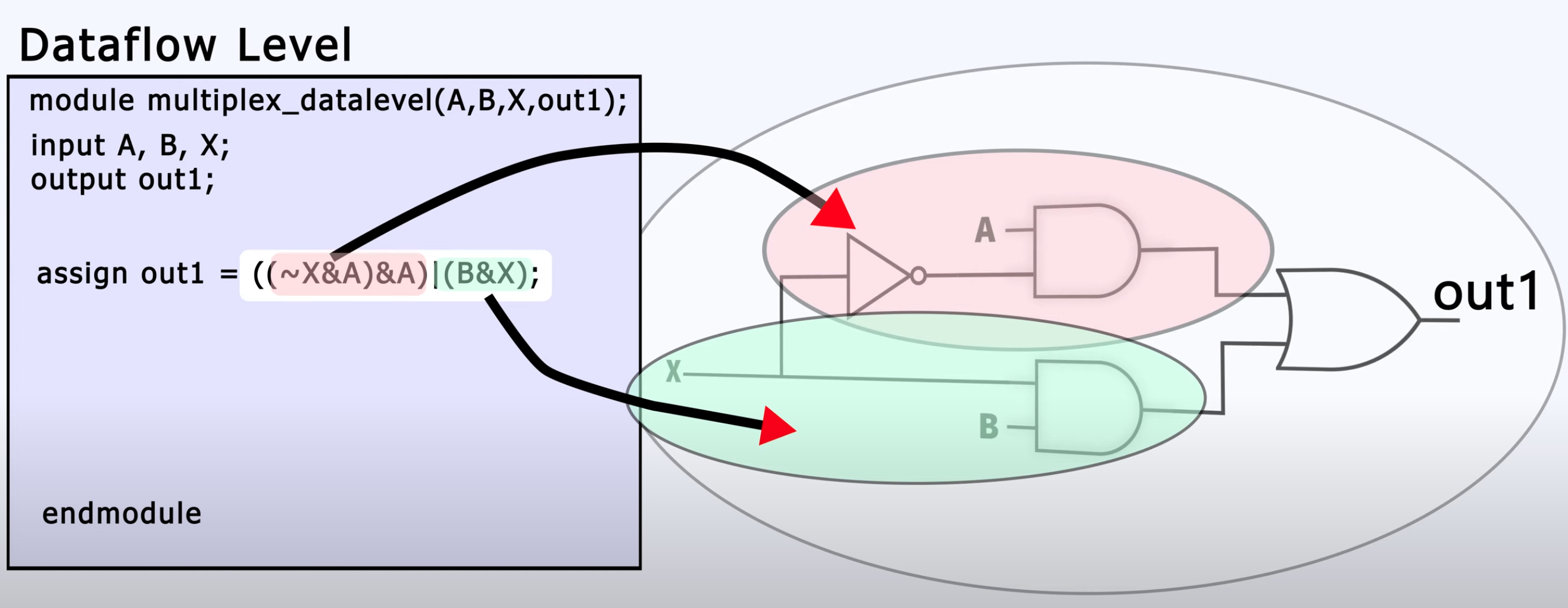
Dataflow Level
Sequential Logic
Sequential logic uses memory and state