Java Web Tokens: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Created page with "=Introduction= Java Web Tokens are used for Authorisation and Information Exchange. They consist of three parts, a header, Payload and a Signature. For example ==Format== ===H..." |
|||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
===Example=== | ===Example=== | ||
[[File:Encoded-jwt3.png|400px]] | [[File:Encoded-jwt3.png|400px]] | ||
=Refresh Tokens= | |||
When the use authenticates they are provided with an access token. The user can then request a new access token with a refresh token. The access token typically has a much shorter lifespan. | |||
[[File:Jwt Refresh.png|200px]] | |||
Revision as of 23:09, 31 March 2021
Introduction
Java Web Tokens are used for Authorisation and Information Exchange. They consist of three parts, a header, Payload and a Signature. For example
Format
Header
{
"alg": "HS256",
"typ": "JWT"
}
Payload
{
"sub": "1234567890",
"name": "John Doe",
"admin": true
}
Signature
HMACSHA256(
base64UrlEncode(header) + "." +
base64UrlEncode(payload),
secret)
Example
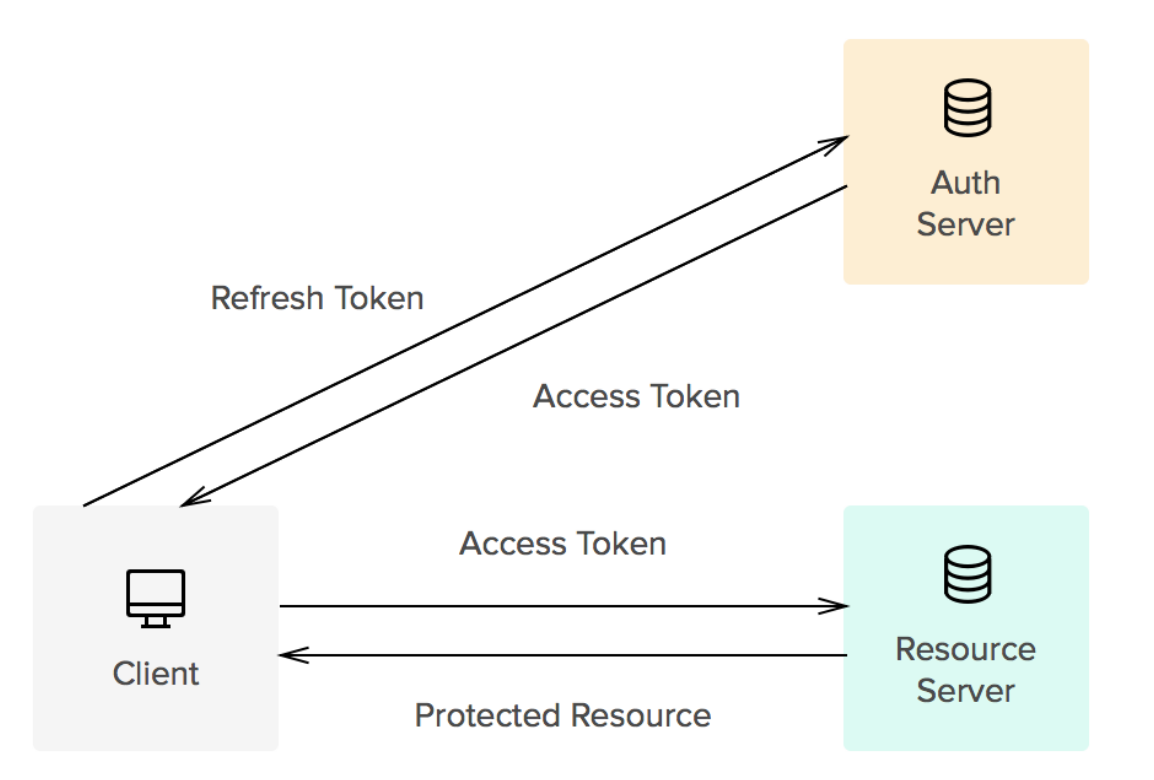
Refresh Tokens
When the use authenticates they are provided with an access token. The user can then request a new access token with a refresh token. The access token typically has a much shorter lifespan.